
Thebrain mcgill ca how to#
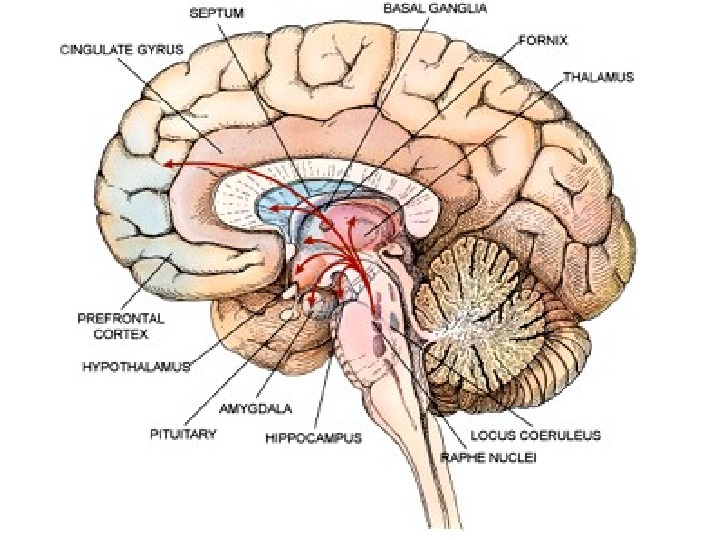
How to retrain: Engage regularly in mindfulness meditation, focusing on your breathing and the sensations in your body. Originates: Signals between the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala. Definition: The ability to recover from adversity. Six emotional dimensions that shape our lives and determine how we respond to our environment and the people around us, based on activity in the brain. Provides emotional context to experience and interprets bodily states such as hungers and cravings.Įmotional Styles - How to Retrain Your Brain Conduct electrochemical messages throughout the brain via a network of trillions of nerve fibers Work with the hypothalamus in the production and distribution of hormones controlling hunger, growth and sex drive connected to the hypothalamus Receives and distributes sensory information from throughout the body to various parts of the brain Stores and retrieves memories processes stimuli, provides context to those situations and relays that information to the amygdala. Influences emotional responses as part of the limbic system, regulates hormone secretion Aids in perception of emotions in others. Acts as the emotional processing center of the brain, responding to stimuli, especially danger like a built-in alarm system. Responsible for abstract analysis, cognitive analysis and the exercise of judgment Controls primitive, survival-based emotions Processes sounds and emotional responses, provides visual perception and maintains certain functions associated with memory Masterminds complex mental processes including emotions Responsible for emotional and artistic expression as well as most functions on the left side of the body Houses the parts of the brain that control and relate to emotions These maps provide an overview of the major areas of the brain involved in processing emotions. The emotional functions of the brain are interwoven at many levels. The brain, which is a much more flexible organ that previously thought, can be consciously retrained to be more emotionally flexible, understanding and sensitive. This work is yielding fascinating insights that we can use to understand how we react to situations and people. Language and music are specialized human modes of communication, which at their core, involve perceptually discrete elements organized into hierarchically structured sequences that give rise to different degrees of meaning. Our global objective is to foster a research and training environment that supports innovative cognitive, cultural, and neuroscientific approaches that gather unique insights into the organization of the human brain for speech, language, music and communication.īringing together a critical mass of researchers with complementary interests and expertise in brain, language, and music, both human and animal models of their function and dysfunction, the CRBLM represents the largest concentration of basic and applied research internationally on this interdisciplinary enterprise.Embed this infographic on your site! Image source: The editors at Best Psychology Degrees Rankings and Reviews decided to research the topic of: The Brain: A User's Guide to EmotionsĪs neuroscience researchers work to unravel the inner workings of the brain, we know more than ever before about the mysteries of where emotions originate in the brain and the connections between instinct, intelligence and emotion. The Centre for Research on Brain, Language and Music – CRBLM – is a strategic research group with a unique interdisciplinary focus on language, music, and their intersection. Centre for Research on Brain, Language and Music


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
